【编辑推荐】2024年3期科研论文、新能源
科研论文

李涛,柳伟∗,邵琛琛,李清萍
(中国海洋大学材料科学与工程学院,山东青岛 266100)
摘要:本文作者通过两步电沉积法制备了具有较好倍率性能和循环稳定性的过渡金属硫化物/氢氧化物异质结构复合电极。首先,在碳布基底上电沉积了一层均匀的镍层,优化了活性物质与碳布之间的附着效果,从而提升了电极的导电性和机械稳定性。随后,在Zn(NO3)2·7H2O的硫代乙酰胺溶液中进行二次电沉积。通过两步电沉积法,在镍层表面形成了掺杂Zn2+的硫化物/氢氧化物异质结构(NCS-Zn-2)。这种复合材料在1A/g的电流下展示了2703F/g的高比电容,并且能够在150 A/g的高电流下保持40.8%的比电容,证明了其优良的快速充放电能力。以NCS-Zn-2为正极,活性炭为负极,应用于1.6 V的水系不对称超级电容器中,在794 W/kg的高比功率下展现了79.9W·h/kg的高比能量。以20A/g电流在0~1.6V循环20 000 次,该电极的电容保持率高达98.7%,显示了较好的循环稳定性。
The performance of Zn2+ doped sulfide / hydroxide heterogeneous structure
LI Tao,LIU Wei ∗ ,SHAO Chenchen,LI Qingping
(School of Material Science and Engineering,Ocean University of China,Qingdao,Shandong 266100,China)
Abstract:Transition metal sulfide/hydroxide heterogeneous structure composite electrodes with good rate capability and cycle stability are prepared by a two-step electrodeposition method. Firstly, a uniform nickel layer is electrodeposited on a carbon cloth substrate to optimize the adhesion effect between the active substance and the carbon cloth, thus enhancing the conductivity and mechanical stability of the electrode. Subsequently, secondary electrodeposition is carried out in a thioacetamide solution of Zn(NO3)2·7H2O. A Zn2+ doped sulfide/hydroxide heterogeneous structure (NCS-Zn-2) is formed on the surface of the nickel layer by the two-step electrodeposition method. This composite demonstrates a high specific capacitance of up to 2 703 F/g at a current of 1 A/g and is able to maintain a specific capacitance of 40.8% at a high current of 150 A/g, proving its good fast charging and discharging capabilities. Using NCS-Zn-2 as the cathode and activated carbon as the anode in a 1.6 V aqueous asymmetric supercapacitor, a high specific energy of 79.9 W·h/kg is demonstrated at a high specific power of 794 W/kg. The capacitance retention of the electrode is as high as 98.7% after 20 000 cycles in 0-1.6 V at 20 A/g, demonstrating its good cycle stability.
引用格式
李涛,柳伟,邵琛琛,等. Zn2+掺杂硫化物/ 氢氧化物异质结构的性能[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):297-302.
LI T,LIU W,SHAO C C,et al. The performance of Zn2+ doped sulfide/ hydroxide heterogeneous structure[J] . Dianchi(Battery Bimonthly),2024,54(3):297-302.(点此下载文章全文)

蔡永华1,2,3,4∗ ,罗子贤1,2,3,4 ,胡健平1,2,3,4
(1. 武汉理工大学现代汽车零部件技术湖北省重点实验室,湖北武汉 430070; 2. 汽车零部件技术湖北省协同创新中心,湖北武汉 430070; 3. 新能源与智能网联车湖北省工程技术研究中心,湖北武汉 430070; 4. 武汉理工大学汽车工程学院,湖北武汉 430070)
摘要:本文作者设计了阴极流道侧壁布置斜挡板的质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)模型,对电池内部压力、氧气浓度和水浓度的分布进行分析。探讨斜挡板的布置方式、堵塞率和夹角对燃料电池性能的影响,并考虑了与反应气体供应相关的泵送功率因素,以最大化燃料电池的净功率输出。
首先,研究挡板布置方式对电池性能的影响,分别建立了阴极侧边挡板的布置方式为无挡板、对置布置和交错布置的单直流道模型,挡板堵塞率均为90%。各模型的极化曲线和净功率密度曲线如图1所示。数据表明,在PEMFC阴极流道侧边安装挡板,可提高电池净功率密度并拓宽电流密度范围,且交错布置的安装方案对电池性能提升的幅度更大,交错模型和对置模型的最大净功率密度较无挡板模型分别提升了13.74%和10.64%。
然后,在阴极流道挡板布置方式选取交错布置的基础上,分别建立堵塞率为50%、70%、90%和95%的单直流道电池模型,与无挡板模型进行对比。不同挡板堵塞率下电池模型的极化曲线和净功率密度曲线如图2所示,由图可知,挡板堵塞率越高,电池性能提升越明显。其中,95%堵塞率模型的净功率密度最高,为1.053 W/cm2,较无挡板模型提升了14.58%,且直到电流密度提升至2.8 A/cm2时,仍未出现明显的浓差极化。这说明提高挡板堵塞率,不仅能实现更高的净功率密度,还能拓宽极限电流密度。
最后,选用堵塞率为95%的挡板交错布置在阴极流道两侧,研究挡板与水平方向的夹角对模型的影响。建立挡板夹角为15°、30°、45°和60°的模型,与未安装挡板的直流道模型作对比。不同挡板夹角下电池模型的极化曲线和净功率密度曲线如图3所示,由图可知,电池的净功率密度与夹角角度并非正相关关系,净功率峰值由高到低排列依次为:15°夹角模型、30°夹角模型、60°夹角模型、45°夹角模型、无挡板模型。
综上所述,当流道内以交错安装的方式布置挡板,挡板堵塞率为95%,夹角为15°时,电池性能最佳,该模型的最大净功率密度较无挡板的直流道模型提升了约14.53%。
Effect of flow fields with horizontal baffle on performance and mass transport of fuel cells
CAI Yonghua 1,2,3,4∗ ,LUO Zixian 1,2,3,4 ,HU Jianping 1,2,3,4
(1. Hubei Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Automotive Components,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan,Hubei 430070,China; 2. Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Automotive Components Technology,Wuhan,Hubei 430070, China; 3. Hubei Technology Research Center of New Energy and Intelligent Connected Vehicle Engineering,Wuhan,Hubei 430070,China; 4. School of Automotive Engineering,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan,Hubei 430070,China)
Abstract:A proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) model with oblique baffles arranged on the sidewalls of the cathode flow channel is studied, and the distribution of internal pressure, oxygen concentration, and water concentration is analyzed. The effects of baffle arrangement, blockage ratio, and angular orientation on fuel cell performance are investigated, considering the pumping power associated with the supply of reactant gases to maximize the net power output of the fuel cell.
Initially, the impact of baffle arrangement on cell performance is studied by establishing single straight channel models with cathode side baffles arranged in no-baffle, opposed, and staggered configurations, all with a 90% blockage ratio. The polarization curves and net power density curves of each model are shown in Fig.1. The data indicate that installing baffles on the sidewalls of the PEMFC cathode channel can enhance the net power density and broaden the range of current densities, with the staggered arrangement offering a greater improvement in performance, increasing the maximum net power density by 13.74% and 10.64% for the staggered and opposed models respectively, compared to the no-baffle model.
Subsequently, based on selecting the staggered arrangement for the cathode channel baffles, single straight channel cell models with blockage ratios of 50%, 70%, 90%, and 95% are established and compared to the no-baffle model. The polarization curves and net power density curves of the different baffle blockage ratios are depicted in Fig.2, showing that higher blockage ratios lead to more significant performance enhancements. Among these, the 95% blockage ratio model achieves the highest net power density of 1.053 W/cm², which is a 14.58% increase compared to the no-baffle model, and it maintains high performance up to a current density of 2.8 A/cm² without significant concentration polarization. This suggests that a higher blockage ratio not only achieves higher net power densities but also extends the limit of current density.
Finally, a 95% blockage ratio with baffles staggered on both sides of the cathode channel is chosen to study the impact of the angle between the baffles and the horizontal direction. Models with baffle angles of 15°, 30°, 45°, and 60° are established and compared to a straight channel model without baffles. The polarization curves and net power density curves of the different baffle angles are shown in Fig.3, indicating that the net power density of the cell is not directly correlated with the angle of the baffles. The net power peaks, from highest to lowest, are arranged as follows: 15° angle model, 30° angle model, 60° angle model, 45° angle model, and no-baffle model.
In summary, the best cell performance is achieved when baffles are staggered in the flow channel with a 95% blockage ratio and a 15° angle, with the maximum net power density of this model increasing by approximately 14.53% compared to the straight channel model without baffles.
引用格式
蔡永华,罗子贤,胡健平. 水平挡板流场对燃料电池性能与传质的影响[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):303-308.
CAI Y H,LUO Z X,HU J P. Effect of flow fields with horizontal baffle on performance and mass transport of fuel cells[J].Dianchi(Battery Bimonthly),2024,54(3):303-308.(点此下载文章全文)

王兴宇,王垣衡,闫佳昕,左朋建∗
(哈尔滨工业大学化工与化学学院,黑龙江
哈尔滨 150001)
摘要:钠在地球上的高资源储备预示着钠离子电池在储能领域的优秀潜力,焦磷酸铁钠(Na2FeP2O7)具备热稳定性和空气稳定性好、原材料来源广泛、价格低廉和循环寿命长等优势,作为正极材料在钠离子电池市场具有很广阔的应用前景。以蔗糖作为碳源,通过溶胶凝胶工艺制备的前驱体,经过惰性气氛高温烧结,可实现Na2FeP2O7正极材料的原位碳包覆,在循环过程中显示出优秀的稳定性,经过恒电流间歇滴定法(GITT)与电化学阻抗(EIS)测试发现,材料Na+扩散系数提升,电池阻抗明显下降。铁源分别为FeSO4·7H2O和Fe(NO3)3·9H2O制备的电极材料,以1.0 C在1.5~4.2 V循环300次后,可分别够保留72 mAh/g与74 mAh/g的放电容量,容量保持率为91.6%与95.1%。碳包覆后的材料在20.0 C下发挥出超过48 mAh/g的放电容量,展示出良好的倍率性能。通过结构和电化学测试证明,形成碳包覆结构可以显著提高焦磷酸铁钠材料的电化学性能。
Effect of iron source precursor on
sodium-ion battery material Na2FeP2O7 / C
WANG Xingyu,WANG Yuanheng,YAN
Jiaxin,ZUO Pengjian ∗
(School of Chemistry and Chemical
Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin,Heilongjiang 150001,China)
Abstract: The high resource reserve of sodium
on the earth indicates the excellent potential of sodium-ion batteries in the
field of energy storage, sodium ferric pyrophosphate (Na2FeP2O7)
has the advantages of good thermal stability and air stability, a wide source
of raw materials, low price, and long cycle life, thus has a broad application
prospect as a cathode material in the sodium-ion battery market. The precursor
prepared by the sol-gel process using sucrose as a carbon source can achieve
in-situ carbon coating of NaFeP2O7 cathode material after
high-temperature sintering in an inert atmosphere, showing excellent stability
during the cycle. Galvanostatic intermittent titration technique (GITT) and
electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) tests show that the diffusion coefficient
of Na+ of the material is increased, and the battery impedance is
significantly decreased. The electrode materials prepared with iron sources as
FeSO4·7H2O and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O
can retain 72 mAh/g and 74 mAh/g respectively after 300 cycles at 1.0 Cin 1.5-4.2 V, and the capacity retention rates are 91.6% and 95.1%. The
carbon-coated material has a discharge capacity of more than 48 mAh/g at 20.0 C,
showing good rate capability. Through structural and electrochemical tests, it
is proved that the electrochemical performance of sodium ferric pyrophosphate
materials can be significantly improved by the formation of carbon-coated
structures.
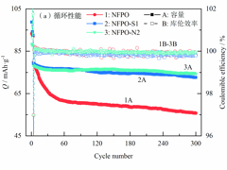
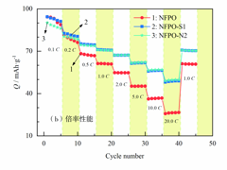
(a)循环性能;(b)倍率性能
图1 NFPO、NFPO-S1与NFPO-N2的电化学性能
Fig.1 Electrochemical performance
of NFPO, NFPO-S1 and NFPO-N2
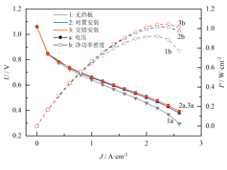
图1 不同挡板布置下电池的性能
Fig.1 Cell performance
with different baffle arrangements
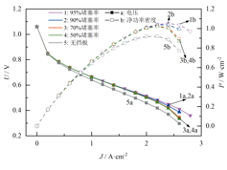
图2 不同挡板堵塞率下电池的性能
Fig.2 Cell performance
with different baffle blockage ratios
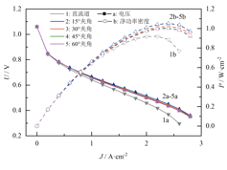
图3 不同挡板夹角下电池的性能
Fig.3 Cell performance
with different baffle angle
引用格式
王兴宇,王垣衡,闫佳昕,等. 铁源前驱体对钠离子电池材料Na2FeP2O7/C 的影响[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):309-314.
WANG X Y, WANG Y H, YAN J X, et al. Effect of iron source precursor on
sodium-ion battery cathode material Na2FeP2O7/C
[J]. Dianchi(Battery Bimonthly),2024,54(3):309-314.(点此下载文章全文)

刘新宝∗ ,余波,覃韬,李萌
(贵州梅岭电源有限公司,特种化学电源国家重点实验室,贵州遵义 563003)
摘要:锌银蓄电池具备安全性高、可靠性高、对环境要求不严格等特点,是空间电源的理想选择。锌银蓄电池在工作过程中的放电电压较平稳,随着电池容量的消耗,进入放电末期时,放电电压会迅速下跌至工作电压下限,电池容量几乎完全放出。锌银蓄电池的放电截止电压一般设计为1.30 V,在该电压下,正极活性物质AgO几乎完全转化为Ag,电池在该状态下贮存一段时间后,再进行充电,充电容量会低于设计容量,该问题的存在大大影响着多周次循环使用的锌银蓄电池性能。本文作者对密封和非密封两种状态的锌银单体蓄电池进行放电态贮存和充电测试,探究放电态贮存对锌银蓄电池充电性能影响。
对两种状态的锌银蓄电池进行放电处理,使其处于放电态,贮存3个月进行充电测试,研究放电态贮存对锌银蓄电池充电性能影响。实验发现,密封单体电池经过贮存后无法充入容量;非密封单体电池在放电态贮存后,充入容量为5.46 Ah,远远小于放电容量,且经过放电态贮存后,电池发生了形变。进一步对原因进行分析,对电池的形貌、微观、内部成分等进行测试,通过测试结果对电池放电态贮存过程中的变化进行分析,微观下,贮存前后的极板表面形貌发生了明显的变化,推断放电态贮存后充入容量不足的原因在于电池内部的电解液分布发生变化。为进一步进行验证,后续补充了补加电解液和夹具实验,实验结果证明了电池贮存后充电容量不足的主要原因在于电解液分布发生了变化。
通过对2种状态电池的对比分析,探究了电池放电态贮存后,充电容量不足的机理,通过该研究可以为多周次使用的锌银蓄电池提供参考。
Charging performance of zinc-silver
battery after storage in the discharge state
LIU Xinbao ∗
,YU Bo,QIN
Tao,LI Meng
(State Key Laboratory of Advanced
Chemical Power Sources,Guizhou Meiling Power Sources Co.,Ltd.,Zunyi,Guizhou
563003,China)
Abstract: The
zinc-silver storage battery has the characteristics of high safety, high
reliability, and no strict environmental requirements, which is the ideal
choice for space power supply. The discharge voltage of the zinc-silver battery
in the working process is relatively stable, and with the consumption of the
battery capacity, the discharge voltage will rapidly fall to the lower limit of
the working voltage when entering the end of the discharge, and the battery
capacity is almost completely released. The discharge cutoff voltage of the
zinc-silver battery is generally designed to be 1.30 V. Under this voltage, the
cathode active substance AgO is almost completely transformed into Ag. After
the battery is stored in this state for a period, the charging capacity will be
lower than the designed capacity, which greatly affects the performance of the
zinc-silver battery used in multi-week cycles. In this paper, the effects of
discharge storage on the charging performance of zinc-silver batteries are investigated
by conducting discharge storage and charging tests on sealed and unsealed
zinc-silver batteries.
Two kinds of zinc-silver batteries are discharged to
make them in a discharge state and stored for 3 months for charging test to
study the effect of discharge state storage on the charging performance of
zinc-silver batteries. It is found that the sealed single battery cannot be
charged after storage. After storage in the discharge state, the charged
capacity of the unsealed single battery is 5.46 Ah, which is far less than the
discharge capacity, and after storage in the discharge state, the battery deformation
occurs. The reasons are further analyzed, and the morphology, microstructure,
and internal composition of the battery are tested. The changes in the storage
process of the battery discharge state are analyzed according to the test
results. At the microscopic level, the surface morphology of the plate before
and after storage changes significantly, and it is inferred that the
insufficient capacity after storage of the discharge state is due to the change
in the distribution of the electrolyte inside the battery. For further
verification, the experiments of replenishment electrolytes and fixtures are
followed, and the experimental results prove that the main reason for the
insufficient charging capacity of the battery after storage is the change of
electrolyte distribution.
The mechanism of insufficient charging capacity after
storage in the discharge state is explored through the comparative analysis of
two kinds of batteries. This study can provide a reference for zinc-silver
batteries used for multi-cycle.
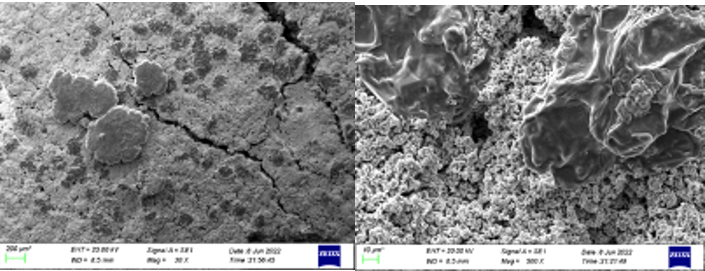
(a)a组低倍率;(b)a组高倍率
图1 贮存后非密封单体电池正极形貌
Fig.1 Cathode morphology of unsealed single battery after storage
引用格式
刘新宝,余波,覃韬,等. 锌银蓄电池放电态贮存后的充电性能[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):315-319.
LIU X B,YU B,QIN T,et al. Charging performance of zinc-silver battery
after storage in discharge state[J] . Dianchi(Battery
Bimonthly),2024,54(3):315-319.(点此下载文章全文)

周梦硕1,罗海洋1,冯振1,2,3∗ ,苏光1,2
(1. 河南工学院材料科学与工程学院,河南
新乡 453003; 2. 河南省金属材料改性技术工程技术研究中心,河南
新乡 453003; 3. 河南师范大学物理学院,河南新乡 453007)
摘要:质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)在能源领域一直备受瞩目,其优势在于结构设计的精巧、能源转化的高效性、产物的清洁性,但较高的贵金属催化剂成本以及耐用性等问题阻碍了其商业化应用。采用金属有机框架(MOF)来替换贵金属材料,并通过应变工程来调节催化剂催化性能。采用第一性原理计算方法,构建出一种氧配位的MOF模型,分别研究x方向和y方向不同应变程度对铁基MOF中心原子氧还原催化活性的影响。这种铁基MOF的中心原子与氧之间形成的特殊配位结构,为氧还原反应(ORR)提供了潜在的活性位点。通过分析在不同电压下x方向和y方向的MOF的ORR自由能图,得到沿宽度y轴方向压缩应变2%到拉伸应变4%的范围内,应变对Fe-O-MOF的催化活性有较大的调节作用。沿金属原子结构长度x轴方向在压缩应变2%到拉伸应变6%的范围内,应变对Fe-O-MOF的催化活性有较大的调节作用。研究成果不仅为PEMFC催化剂的设计提供了思路,也为其他领域的催化剂开发提供了方法。通过精确调控MOF的应变,可以实现对催化剂性能的精准控制,从而为其在能源、环境等领域的应用奠定坚实的基础。
Effect of strain
control on metal-organic frameworks electrode activity in PEMFC
ZHOU Mengshuo 1,LUO Haiyang 1 ,FENG Zhen 1,2,3∗ ,SU Guang 1,2
(1. School of Materials
Sciences and Engineering,Henan Institute of Technology,Xinxiang,Henan
453003,China;2. Henan Engineering Research Center for Modification Technology
of Metal Materials,Xinxiang,Henan 453003,China; 3. School of Physics,Henan
Normal University,Xinxiang,Henan 453007,China)
Abstract:Proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) has been attracting much attention
in the field of energy. Its advantages lie in its exquisite structural design,
high efficiency of energy conversion, and cleanliness of products. However, the
high cost and durability of precious metal catalysts hinder its commercial
application. The metal-organic framework (MOF) is used to replace the noble
metal material, and the catalytic performance of the catalyst is adjusted by
strain engineering. A MOF model of oxygen coordination is constructed using the
first principles method. The effects of different strain degrees in the x
direction and y direction on the catalytic activity of atomic oxygen reduction
in the center of iron-based MOF are studied. The special coordination structure
formed between the central atom of this iron-based MOF and oxygen provides a
potential active site for oxidation-reduction reaction (ORR). By analyzing the
ORR free energy diagram of MOF in x and y directions at different voltages, it
is found that the strain has a great regulating effect on the catalytic
activity of Fe-O-MOF in the range of 2% compressive strain to 4% tensile strain
along the y-axis. The catalytic activity of Fe-O-MOF is significantly regulated
by strain in the range from 2% to 6% of compressive strain along the x-axis of
metal atomic structure length. The research results not only provide an idea
for the design of PEMFC catalysts but also provide a method for the development
of catalysts in other fields. By precisely adjusting the strain of MOF, the
precise control of catalyst performance can be achieved, thus laying a solid
foundation for its application in energy, environment, and other fields.
引用格式
周梦硕,罗海洋,冯振,等. 应变调控对PEMFC金属有机框架电极活性的影响[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):320-324.
ZHOU M S,LUO H Y,FENG Z,et al. Effect of strain control on metal-organic
frameworks electrode activity in PEMFC[J].Dianchi(Battery
Bimonthly),2024,54(3):320-324. (点此下载文章全文)

岳姗1 ,智茂永1,2∗ ,郑玲玲1 ,苏柄键1
(1. 中国民用航空飞行学院民航安全工程学院,四川
德阳 618307; 2.民机火灾科学与安全工程四川省重点实验室,四川德阳 618307)
摘要:由于锂离子电池具有能量密度高、使用寿命长等特点,已成为电动汽车和电动飞行器的主流储电部件。电池在充放电过程中发生的电化学反应会产生一定的热量,当电池产热速率大于散热速率时,可能导致热失控现象,电池散热问题是制约电池安全运行的重要课题。因此,电池热管理是商业化锂电池系统不可或缺的组成部分。传统的风冷或液冷散热方式在散热效率、温度均匀性和安装维护等方面存在局限性,而相变材料冷却具有结构简单、温度均匀性好以及维护成本低等优点,得到越来越多的关注。本文作者研究了聚乙二醇(PEG)基相变材料在锂离子电池热管理中的应用。采用熔融共混法,以PEG和膨胀石墨为原料制备复合相变材料,并通过实验研究了其热物理性质和电池热管理性能。随着膨胀石墨添加量的增加,相变材料的熔点和热焓都有所降低,而导热系数则相应提高。当膨胀石墨的质量分数为10%时,复合相变材料的熔点、热焓和导热系数分别为46.8 ℃、116.6 J/g和1.379 W/(m·K)。在电池热管理性能测试中,相变材料冷却能较好控制电池温度,在2.0 C放电倍率下,与风速为2.3 m/s的强制空气冷却相比,单体电池和电池组的最高温度分别降低了7.15 ℃和10.98 ℃。此外,通过傅立叶红外光谱、SEM和差示扫描量热仪等测试手段,分析了相变材料的结构、微观形貌和储热性能。实验结果表明,复合相变材料中的PEG4000与膨胀石墨为物理混合,并未发生化学反应,并且相变材料具有良好的形状稳定性和抗泄漏性能。在电池热管理应用中,复合相变材料展现出了优异的热管理效果,有望提高电池的安全性能并延长其使用寿命。
Polyethylene glycol-based
phase change materials for battery thermal management
YUE Shan 1 ,ZHI Maoyong 1,2∗ ,ZHENG
Lingling 1 ,SU Bingjian 1
(1. College of Civil Aviation
Safety Engineering,Civil Aviation Flight University of China,Deyang,Sichuan
618307,China; 2. Civil Aircraft Fire Science and Safety Engineering Key
Laboratory of Sichuan Province,Deyang,Sichuan 618307,China)
Abstract: Due to its high energy density and
long service life, Li-ion batteries have become the mainstream energy storage
components for electric vehicles and aircraft. The electrochemical reaction of
batteries occurs during the charging and discharging process, a certain amount
of heat is generated. When the heat generation rate of the battery exceeds the
heat dissipation rate, thermal runaway may happen. The problem of battery heat
dissipation is an important issue that restricts the safe operation of the
battery. Therefore, battery thermal management is an indispensable component of
commercial Li-ion battery systems. Traditional air-cooled or liquid-cooled cooling
methods have limitations in terms of heat dissipation efficiency, temperature
uniformity, and installation and maintenance. However, phase change material
cooling has gained increasing attention due to its advantages of simple
structure, good temperature uniformity, and low maintenance costs.
The application of polyethylene glycol (PEG) based phase change materials in the thermal management of Li-ion batteries is investigated. Composite phase change materials are prepared using the melt blending method with PEG and expanded graphite as raw materials, and their thermal physical properties and battery thermal management performance are studied through experiments. The melting point and enthalpy of phase change materials decrease with the amount of expanded graphite increasing, while the thermal conductivity increases accordingly. When the mass fraction of expanded graphite is 10%, the melting point, enthalpy, and thermal conductivity of composite phase change material are 46.8 ℃, 116.6 J/g, and 1.379 W/(m·K), respectively. In the thermal management performance test of batteries, phase change material cooling can better control the battery temperature. At a discharge rate of 2.0 C, compared with forced air cooling with a wind speed of 2.3 m/s, the maximum temperature of individual batteries and battery packs decreases by 7.15 ℃ and 10.98 ℃, respectively. In addition, the structure, microstructure, and thermal storage performance of phase change materials are analyzed through testing methods such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, SEM, and differential scanning calorimetry. The experimental results show that the PEG4000 in the composite phase change material is a physical mixture with expanded graphite, without any chemical reaction, and the phase change material displays good shape stability and leakage resistance. In the application of battery thermal management, composite phase change materials also show excellent thermal management effects, which are expected to improve the safety performance of batteries and extend their service life.
引用格式
岳姗,智茂永,郑玲玲,等. 聚乙二醇基相变材料用于电池热管理[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):325-329.
YUE S,ZHI M Y,ZHENG L L,et al. Polyethylene glycol based phase change
materials for battery thermal management[J]. Dianchi(Battery
Bimonthly),2024,54(3):325-329.(点此下载文章全文)

吴军1 ,邱申1 ,胡庆波1 ,徐艳辉2∗
[ 1. 联翼(泰兴)新能源有限公司,江苏
泰州 225400; 2. 苏州大学钢铁学院,江苏
苏州 215006 ]
摘要:为考察负极黏结剂对锂离子电池性能的影响,分别以丁苯橡胶(SBR)、改性SBR、苯乙烯丙烯酸酯(SA)为负极黏结剂,制备锂离子电池,并对电池的性能进行评估。结果表明:SA类黏结剂在内阻、低温放电及循环性能上优于传统的SBR黏结剂。首先,SA类黏结剂在负极颗粒表面分布更加均匀(见图1),有利于改善充放电过程中离子的迁移,对锂离子电池内阻特性有明显改善,在25 ℃下,SA黏结剂制备电池的直流内阻(DCR)为28.68 mΩ,比SBR黏结剂制备的电池下降了22.08%,-20 ℃下则下降了26.26%;其次,由于SA类黏结剂较低的内阻特性,使其在低温充放电及大倍率充放电时具有较低的电池极化,在-20 ℃放电性能和25 ℃下2.2 C快充循环上与有明显改善。与SBR黏结剂制备的电池相比,-20 ℃下以1.0 C(2.3 A)放电,保持率提高10.78%,25 ℃下2.2 C快充循环700次,保持率提高9.3%。
Effect of silicon anode binder on
the performance of
Li-ion battery
WU Jun 1 ,QIU Shen1 ,HU Qingbo 1 ,XU Yanhui 2∗
(1. Linktec New Energy
Co.,Ltd.,Taizhou,Jiangsu 225400,China; 2. School of Iron and Steel, Soochow
University,Suzhou,Jiangsu 215006,China)
Abstract: In order to investigate the effect of anode binder on the performance of Li-ion battery, the electrochemical performance of the battery is evaluated, which is prepared with styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), modified SBR and styrene acrylate (SA) as anode binder, respectively. The results show that the SA binder has better performance than the SBR binder in internal resistance, low-temperature discharge, and cycle performance. Firstly, the SA binder is more evenly distributed on the surface of the anode particles (see Fig.1), which is conducive to improving the ion transfer during the charge and discharge, so the SA binder has a significant improvement in the internal resistance characteristics. The direct current resistance (DCR) of the battery with SA binder is 28. 68 mΩ at 25 ℃, which is 22.08% lower than that with SBR binder, and it is 26.26% lower than that of SBR binder at -20 ℃. Secondly, due to the low internal resistance characteristics of the SA binder, it has lower polarization at low-temperature discharge and high-rate cycle performance. Compared with the battery prepared with SBR binder, it is discharged at 1.0 C(2.3 A) at -20 ℃, and the capacity retention was increased by 10.78%, and the capacity retention is increased by 9.3% after 700 fast charging cycles at 2.2 C at 25 °C.
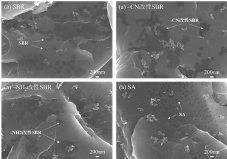
图1 不同黏结剂负极片SEM图
Fig.1 SEM photographs of the anode
with different binders

引用格式
吴军,邱申,胡庆波,等. 硅负极黏结剂对锂离子电池性能的影响[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):330-333.
WU J,QIU S,HU Q B,et al. Effect of silicon anode binder on the performance of Li-ion battery[J] . Dianchi( Battery Bimonthly),2024,54(3):330-333.(点此下载文章全文)

新能源

吕高1 ,樊郭宇1 ,张嘉蕾1∗ ,杜君莉2 ,史书怀2
(1. 山西大学电力与建筑学院,山西
太原 030000; 2. 国网河南省电力公司电力科学研究院,河南
郑州 450000)
摘要:在当前的社会环境下,锂离子电池广泛应用于各个行业,尤其是在无污染、质量轻的新能源电动车领域。对锂离子电池荷电状态(SOC)的精确估计,对提升电池的使用效率和性能有重要的意义。本文作者围绕锂离子电池SOC的估计算法展开研究,进行了如下工作。
现有SOC的估计方法中仅仅加入了温度校正系数,无法得知温度对电池内部各参数的影响,而电池参数的改变又会影响SOC估计的准确度。针对此问题,考虑了温度变化对电池内部参数影响,提出了一种考虑温度的滑模观测法(SMO)进行SOC估计。基于混合脉冲功率特性测试(HPPC)实验得到的详细数据,得到18650型LiFePO4锂离子电池的SOC与温度、参数之间的拟合式,并进行了不同温度条件下的参数辨识。最后,通过台风(Typhoon)系统进行半实物实验分析,结果如图1和图2所示。温度自适应SMO算法在低温或常温工况下的平均误差较传统SMO算法降低了0.3~0.5个百分点。直接通过拟合式所快速估计的SOC较温度自适应SMO算法平均误差在2%左右,常温25 ℃工况下误差低于1%,能够实现较高的估计精准度,为快速估计SOC提供了较好的算法参考。
SOC estimation for Li-ion battery
used by temperature adaptive SMO algorithm
LYU Gao 1 ,FAN Guoyu1 ,ZHANG Jialei 1∗ ,DU Junli 2,SHI Shuhuai 2
(1. School of Electric Power and
Architecture,Shanxi University,Taiyuan,Shanxi 030000,China; 2. Electric Power
Science Research Institute,State Grid Henan Electric Power
Company,Zhengzhou,Henan 450000,China)
Abstract:In the current social environment, Li-ion batteries are
widely used in various industries, especially in the field of pollution-free
and lightweight new energy electric vehicles. Accurate estimation of the state
of charge (SOC) of Li-ion batteries is of great significance for improving
their efficiency and performance. This article focuses on the estimation
algorithm of SOC for Li-ion batteries and conducts the following work.
The existing methods for estimating SOC only include
temperature correction coefficients, which cannot determine the impact of
temperature on various internal parameters of the battery, and changes in
battery parameters can affect the accuracy of SOC estimation. In response to
this issue, the influence of temperature changes on the internal parameters of
the battery is considered, and a sliding mode observer (SMO) method considering
temperature is proposed for SOC estimation. Based on the detailed data obtained
from the hybrid pulse power characterization (HPPC) experiment, a fitting
equation is obtained between the SOC of 18650 type LiFePO4 Li-ion
battery and temperature, parameters, and parameter identification is carried
out under different temperature conditions. Finally, a semi-physical
experimental analysis is conducted using the Typhoon system, and the results
are shown in Fig.1 and Fig.2. The average error of the temperature adaptive SMO
algorithm under low or normal temperature conditions is reduced by 0.3-0.5
percentage points compared to traditional SMO algorithms. The average error of
SOC estimated directly through the fitting equation is about 2% compared to the
temperature adaptive SMO algorithm, and the error is less than 1% at room
temperature of 25 ℃, which can
achieve high estimation accuracy and provide a good algorithm reference for
quickly estimating SOC.
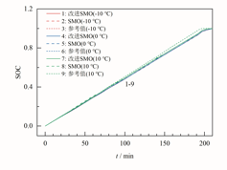
图1 低温下SOC实验结果
Fig.1 Results of state of charge
(SOC) experiment at low temperatures
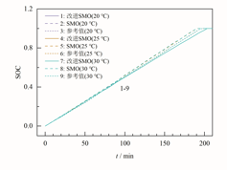
图2 常温下SOC实验结果
Fig.2 Results of SOC experiment at room

引用格式
吕高,樊郭宇,张嘉蕾,等. 温度自适应SMO算法估计锂离子电池的SOC[J].电池,2024,54(3):334-339.
LYU G,FAN G Y,ZHANG J L,et al. SOC estimation for Li-ion battery used by
temperature adaptive SMO algorithm[J].Dianchi(Battery
Bimonthly),2024,54(3):334-339.(点此下载文章全文)

李锦满1 ,李儒欢1 ,李浩南1 ,李存鑫1 ,邱子桐1 ,郭凯2 ,吴锴1 ,周峻1∗
(1. 西安交通大学电气工程学院,陕西
西安 710049; 2. 国网山东省电力科学研究院,山东
济南 250003)
摘要:在电动汽车和储能系统中,电池管理系统(BMS)对于确保电池系统的安全性和可靠性至关重要。BMS的一个核心功能是对动力电池的荷电状态(SOC)和健康状态(SOH)进行准确评估。SOC和SOH的准确预测对于电动汽车电池系统的安全运行至关重要。传统的卡尔曼滤波(KF)算法虽然广泛应用于动力电池状态估计,但存在显著的非线性误差。为了解决这一问题,本文作者提出了一种基于无迹卡尔曼滤波(UKF)的算法,用于实现对动力电池状态的更准确估计。首先,分析了动力电池实验数据,建立了一阶Thevenin等效电路模型,该模型的拟合优度达到了0.992,能够较好地反映电池的内部特性。随后,通过加入容量衰退机制,模拟了锂离子电池的老化过程,并采用恒流充电和随机放电循环来模拟电池在实际使用中的工况。在不同的初始条件及循环次数下,利用UKF算法对SOC和SOH进行了估计,结果显示在所有测试中,估计的均方根误差(RMSE)均小于0.01,并且随着电池循环次数的增加,估计误差呈现逐渐减小的趋势。这表明UKF算法不仅能够提供准确的SOC和SOH估计,而且还具有很好的鲁棒性。为了验证UKF算法的有效性,还将其与传统的安时积分法进行了比较。结果表明,安时积分法随着电池循环次数的增加,其估计误差会不断累积,而UKF算法则能够持续提供稳定的估计性能,即使在多次循环后,估计误差也未见明显增加。
State estimation for power battery
based on unscented Kalman filter
LI Jinman 1 ,LI Ruhuan 1,LI Haonan 1 ,LI Cunxin 1 ,QIU Zitong 1 , GUO
Kai 2 ,WU Kai 1 ,ZHOU Jun 1∗
(1. Department of Electrical
Engineering,Xi’an Jiaotong University,Xi’an,Shaanxi 710049,China; 2. Shandong
Electric Power Research Institute,Jinan,Shandong 250003,China)
Abstract: In electric vehicles and energy storage systems, the battery management system (BMS) is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of the battery system. One core function of the BMS is to accurately assess the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of the power battery. Accurate prediction of SOC and SOH is essential for the safe operation of electric vehicle battery systems. Although the traditional Kalman Filter (KF) algorithm is widely used for power battery state estimation, it suffers from significant nonlinear errors. To address this issue, an algorithm based on the Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) to achieve a more accurate estimation of the power battery state is proposed. Firstly, experimental data of power batteries is analyzed, and a first-order Thevenin equivalent circuit model is established, which achieves a goodness of fit of 0.992, effectively reflecting the internal characteristics of the battery. Then, by incorporating a capacity decay mechanism, the aging process of Li-ion batteries is simulated. Constant current charging and random discharge cycles are used to simulate the actual operating conditions of the battery. Under different initial conditions and cycle numbers, the UKF algorithm is used to estimate SOC and SOH. The results show that in all tests, the root mean square error (RMSE) of the estimates is less than 0.01, and the estimation error decreases gradually with the increase in battery cycle times. It indicates that the UKF algorithm not only provides accurate SOC and SOH estimates but also has good robustness. To validate the effectiveness of the UKF algorithm, it is also compared with the traditional Ampere-hour integration method. The results show that with the increase in battery cycle times, the estimation error of the Ampere-hour integration method continues to accumulate, while the UKF algorithm consistently provides stable estimation performance, with no significant increase in estimation error even after multiple cycles.

引用格式
李锦满,李儒欢,李浩南,等. 基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的动力电池状态估计[J]. 电池,2024,54(3):340-343.
LI J M,LI R H,LI H N,et al. State estimation for power battery based on
unscented Kalman filter[J]. Dianchi( Battery Bimonthly),2024,54(3):340-343.(点此下载文章全文)

往/期/回/顾
点击下方名片 关注我们

欢迎订阅《电池》杂志
扫码关注
微信编辑 汤翊 责编 复审 刘冰 终审 李胜
本刊未委托任何第三方机构或个人代为收费或组稿,作者朋友们请投稿至唯一指定邮箱:dianchi@batterypub.com
-1971年创刊-欢迎转载传播-
版权声明
本文仅作者转发或者创作,不代表旺旺头条立场。
如有侵权请联系站长删除
- 1 亲爱的妳 | 女教师的「智性衣橱」 ...
- 2 NEW IN | 秋风起,印花依旧迷人 ...
- 3 本周活动指南,暑期观影夏令营,萌宠运动会...更多精彩尽在漳州台商万达! ...
- 4 ETF投资知识5 | 手把手教你ETF如何买卖 ETF怎么买?ETF虽然也是基金,但是他的交易方式却等同于股票。因此,想要买卖ETF,首先要有个可以买卖股票的股票账户,还未开通股票账户的投资者可参阅《民生证券开户指南》。然后,投资者们只需要在自己的“民生财富汇App”中输入对应的ETF代...
- 5 根网科技祝您中秋快乐——月满人圆 喜乐安康! 皓月当空,心海澄明君之所想,吾志所向...
- 6 党的二十届三中全会公报一图读懂 来源:新华社免责声明:以上内容基于本公司认为可靠的已公开信息整理形成,民生证券力求但不保证内容的准确性和完整性,不保证已做最新变更。以上内容仅供参考,不构成民生证券做出的投资建议、收益承诺或对任何观点的认可。投资者应自主进行投资决策,民生证...
- 7 四大行,历史新高 预计阅读时间 | 3 分钟正文丨 1053 字今天,银行股持续走高。工商银行、农业银行、中国银行、建设银行均创历史新高,邮储银行再创阶段新高。今年以来,银行股整体表现强势,领涨大盘。据东方财富Choice数据,年初至今,农业银行...
- 8 1F UNDER ARMOUR | 运动就进阶,精选商品低至3折起 ...
- 9 官宣!苹果发布会:9月10日凌晨1点 入手 iPhone 15,现在正是好时机!指定型号立减 1300 元!更多精彩资讯...
- 10 端午休市安排(附国债逆回购攻略) 国债逆回购小贴士1️⃣ 国债逆回购是什么?国债逆回购可以理解为一种短期借贷。通俗地说,你把钱借给别人,获得固定利息;而别人用国债作抵押,到期还本付息。国债逆回购是由交易所交易并进行监管,不会出现到期资金不能归还的情况。历史经验显示,每逢季末...
- 正义判决!宜生无忧声明:前员工敲诈勒索终获十年刑责 5天前
- 春天有XIN事 | 春天来了,这群物业人有什么心事? 5天前
- 美团发布2024年Q4及全年财报:一起更好,Better Together 5天前
- 宜生动态丨宜生无忧受邀参加沈阳残疾人就业洽谈会 5天前
- 国际专家亲诊 | 3月14-15日,英国爱丁堡大学欧山林博士亲诊,国际顶尖水准触手可及,缺牙“即刻重生” 5天前
- 低价陷阱受害者控诉惨痛经历:隐形加价,维权无门 5天前
- 黄陈宏博士转任用友网络董事 5天前
- 元气森林创造营2044:年轻人、创新、热爱、试试 5天前
- 我们邀请您一起共创好产品 5天前
- 打造铁路信号智能运维“超级医生”——“和行”轨道交通大模型让运维更高效 5天前
 旺旺头条
旺旺头条




发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。